Schedule a Visit
Regardless of whether you require general advice or specific support, we are happy to help you.
Regardless of whether you require general advice or specific support, we are happy to help you.
All News
Share
Understanding the classification of danger levels for UV lasers is essential for anyone concerned about safety in environments where these powerful tools are used. Did you know that exposure to UV laser radiation can cause serious eye injuries and skin damage? At OPMT Laser, we recognize your need for clear, actionable information on this topic.
In this article, you will discover how UV lasers are categorized into four distinct classes—each with specific characteristics and safety measures. We’ll break down the implications of these classifications, helping you navigate the potential risks effectively.
Ready to enhance your knowledge and ensure a safer experience with UV lasers? Let’s get started!

Lasers are classified based on their potential for causing immediate injury to the eyes or skin and their ability to ignite flammable materials. The classification system helps users understand the risks associated with different types of lasers, ensuring appropriate safety measures are implemented.
Class I lasers are considered completely safe under normal operating conditions. These lasers emit optical radiation levels that do not exceed exposure limits for the eye, regardless of exposure duration. This inherent safety is achieved through effective shielding mechanisms that prevent any direct exposure to the laser beam. Common examples include:
These devices incorporate interlock systems to ensure users cannot be exposed to laser radiation during operation, making them ideal for everyday use.
Class II lasers operate at an output power of up to 1 milliwatt and primarily emit visible light. They present minimal risk since they typically do not cause skin burns. The natural aversion response of the human eye, such as blinking, provides some protection against brief exposure. However, prolonged staring is discouraged, and these devices should carry “Caution” labels. Examples include:
Users should remain aware of the potential for eye discomfort with extended use.
Class IIIA lasers range from 1 milliwatt to 5 milliwatts in output power. While they usually do not cause skin burns, they can potentially harm the eyes if viewed directly for extended periods. Safety measures for Class IIIA lasers include:
In contrast, Class IIIB lasers have higher output levels, ranging from 5 milliwatts to 500 milliwatts. Direct observation can lead to significant eye damage; therefore, protective eyewear is recommended when using these lasers. Users should also be aware that these devices may pose minor skin hazards.
Class IV lasers are classified as the most hazardous, with output powers exceeding 500 milliwatts. These powerful lasers can cause severe eye damage and skin burns and may ignite flammable materials. Due to their high risk, strict safety protocols must be implemented when using Class IV lasers, including:
Operators must wear appropriate protective gear, such as goggles or body suits, to ensure their safety while working with these high-powered devices.
| Laser Class | Output Power | Eye Safety | Skin Safety | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class I | ≤ 0.5 mW | Safe | Safe | Laser printers, CD players |
| Class II | Up to 1 mW | Minimal risk | Safe | Laser pointers |
| Class IIIA | 1 mW – 5 mW | Potential eye harm | Safe | Some handheld laser devices |
| Class IIIB | 5 mW – 500 mW | Eye damage possible | Minor skin hazards | Industrial laser equipment |
| Class IV | > 500 mW | Severe eye damage | Severe burns possible | High-powered cutting/engraving lasers |
Understanding the classification of UV laser danger levels is crucial for anyone working with these powerful tools. With over 5,000 laser-related injuries reported annually, prioritizing safety is essential. By implementing the right safety measures tailored to each classification, you can significantly reduce risks and ensure a secure environment for your applications.
At OPMT Laser, we are dedicated to empowering you with the knowledge needed to navigate these classifications effectively. Our resources provide valuable insights that help you make informed decisions about laser safety.
Are you ready to enhance your understanding and ensure safe practices? Explore our offerings and discover how OPMT Laser can support your journey towards safer laser usage!
Disclaimer
This content is compiled by OPMT Laser based on publicly available information for reference only; mentions of third-party brands and products are for objective comparison and do not imply any commercial association or endorsement.
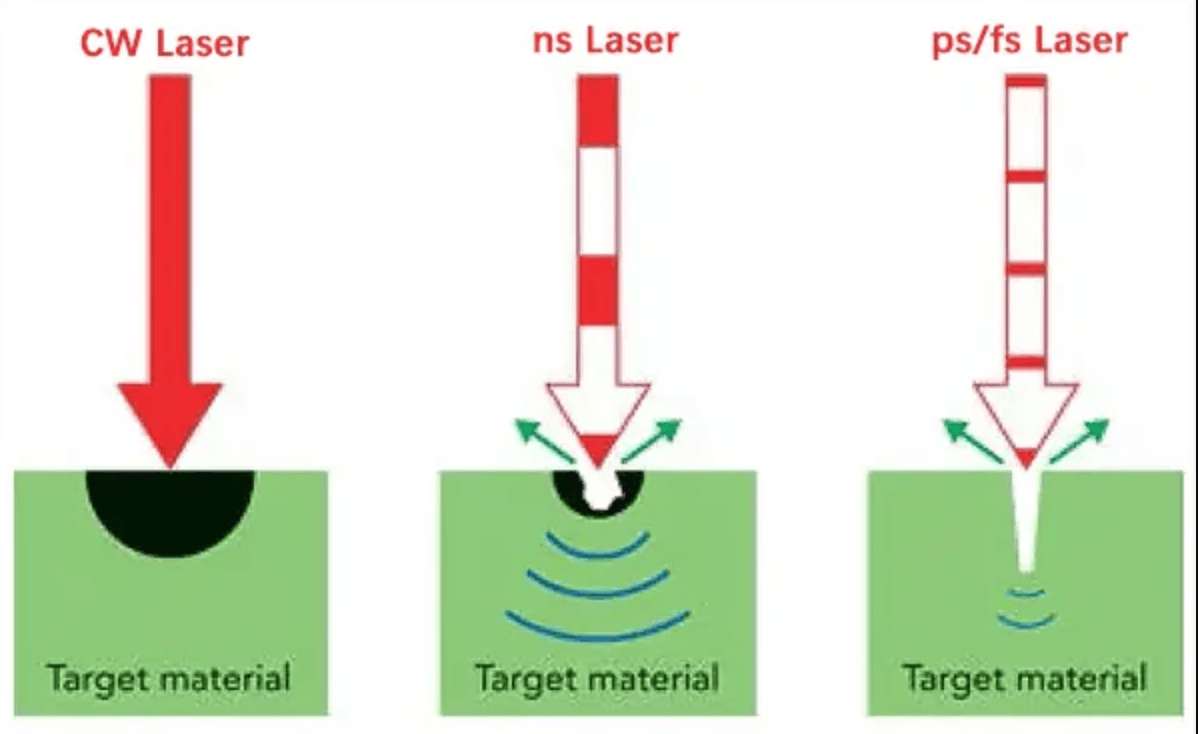
Compare picosecond vs nanosecond laser systems for industrial manufacturing. HAZ data, processing speeds, cost analysis, and application criteria from OPMT’s deployed systems.

PCD laser cutting machines deliver 0.003mm accuracy and 3x faster processing than EDM. Complete technical guide to polycrystalline diamond tool manufacturing for aerospace and automotive industries.
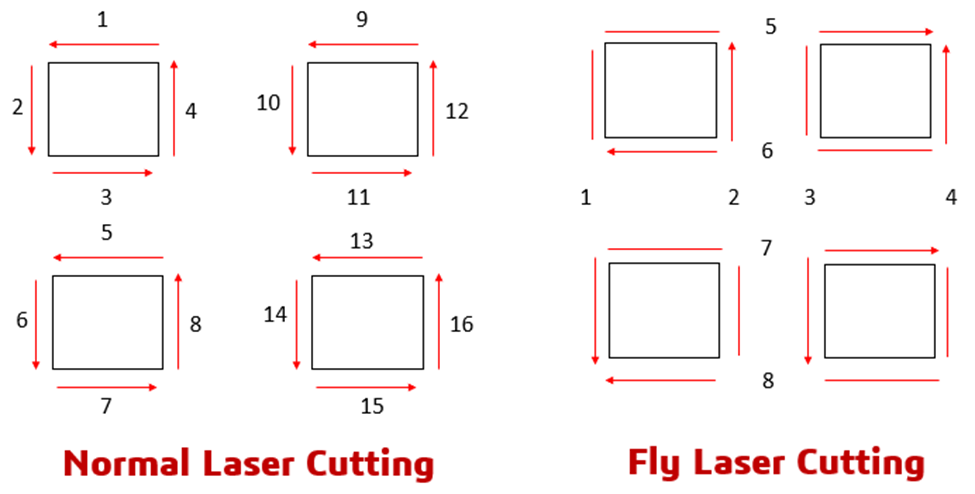
Fly cut laser technology reduces cycle time by 30-50% through continuous motion path optimization. Learn mechanics, applications, and OPMT equipment specifications for precision manufacturing.

Factory evaluation frameworks for laser cutting equipment procurement. Infrastructure assessment, quality systems analysis, and total cost of ownership calculations based on 30+ facility audits.
Please fill in your contact information to download the PDF.

