Handheld laser welding technology represents a significant advancement in the welding industry, offering numerous benefits over traditional methods. This innovative approach utilizes a high-powered laser beam to fuse materials quickly and efficiently, resulting in clean, aesthetically pleasing welds with minimal heat distortion.
Key advantages of handheld laser welders include:
- Speed and Efficiency: These machines can operate up to four times faster than conventional welding methods like MIG and TIG, significantly enhancing production rates.
- Precision and Control: Handheld laser welders provide exceptional accuracy, allowing for intricate welds without the need for extensive post-processing.
- Versatility: Capable of welding various materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, and copper, these machines adapt to diverse applications across multiple industries.
- Reduced Training Time: Their user-friendly design makes it easier for operators to learn and achieve consistent results, even without prior welding experience.
Overall, handheld laser welding is transforming manufacturing processes by delivering high-quality results while minimizing costs and operational complexities.
What is a Handheld Laser Welding Machine?
A handheld laser welding machine is a portable device that utilizes advanced laser technology for non-contact welding. This innovative tool enables users to instantly melt various metals using a concentrated laser beam, which cools rapidly to form strong welds without mechanical pressure. Its portability and versatility make it suitable for a wide range of applications across multiple industries, including automotive, aerospace, and metal fabrication.
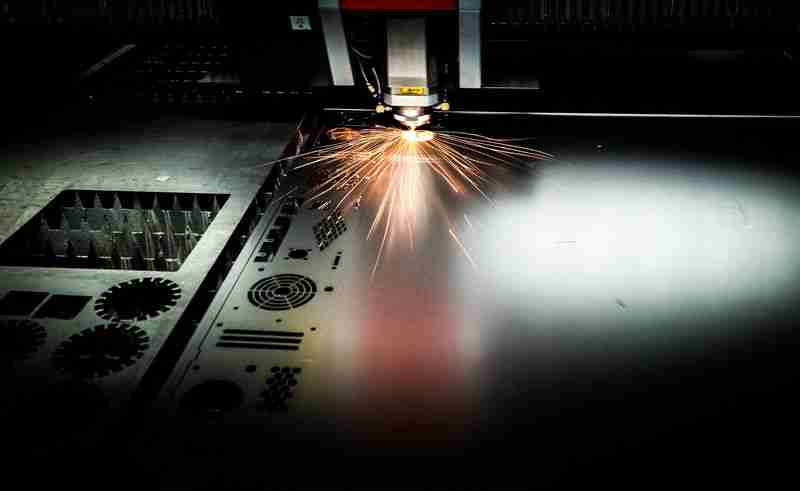

Working Principle
Handheld laser welding machines operate on the principle of localized heating through high-energy laser pulses. This method offers several advantages over traditional welding techniques:
- Enhanced Efficiency: The process is significantly faster, allowing for quick welds.
- Precision: The focused laser beam ensures accurate welding with minimal heat impact on surrounding materials.
- Minimal Heat Affected Zone (HAZ): This reduces thermal distortion, preserving the integrity of the workpiece.
Basic Mechanism
- Laser Generation: The machine generates a focused laser beam, typically produced by fiber or solid-state lasers.
- Localized Heating: The laser beam directs energy to a small area of the workpiece, rapidly raising the temperature to its melting point.
- Melting and Solidification: The intense heat melts the material at the targeted spot. Once the laser is removed, the molten material cools quickly, solidifying into a robust weld joint.
Key Components
A handheld laser welding machine consists of several essential components:
- Control Unit: This unit enables operators to adjust settings such as laser power and pulse duration, often featuring user-friendly interfaces like touchscreens.
- Laser Source: This is the core of the machine, generating the laser beam. Fiber lasers are commonly used due to their efficiency and compact size.
- Handheld Welding Head: Designed for ease of use, this lightweight component includes focusing lenses and a protective nozzle, allowing for maneuverability in various positions.
- Cooling System: To manage heat generated during welding, machines are equipped with either air or water cooling systems.
Advantages of Handheld Laser Welding Machines
Handheld laser welding machines have revolutionized the welding industry by providing numerous advantages over traditional welding methods. These benefits enhance productivity, quality, and operational efficiency across various sectors.
Precision and Quality
- Exceptional Accuracy: Handheld laser welders deliver outstanding precision, making them ideal for intricate applications in fields such as electronics and aerospace, where tight tolerances are essential.
- Minimized Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ): The laser welding process generates significantly less heat, which reduces the heat-affected zone. This feature is particularly advantageous for delicate materials that are sensitive to high temperatures, minimizing the risk of warping or deformation.
- High-Quality Welds: The welds produced are not only smooth but also visually appealing, often eliminating the need for extensive post-welding processes like grinding or polishing. This efficiency saves both time and resources.
Efficiency and Speed
- Rapid Welding Speeds: Handheld laser welding operates 5 to 10 times faster than conventional methods such as TIG and MIG welding. This speed boosts productivity and increases throughput in manufacturing processes.
- Cost-Effective Operations: By reducing labor requirements—one machine can replace multiple welders—and lowering consumable costs, handheld laser welding results in significant operational savings.
Flexibility and Portability
- Versatile Applications: These machines can effectively weld a variety of materials, including stainless steel, carbon steel, and aluminum alloys. They are suitable for diverse applications ranging from automotive components to medical devices.
- User-Friendly Design: Designed for ease of use, handheld laser welders allow operators to work at different angles and positions. This flexibility is ideal for large or immobile workpieces.
- Portable Construction: Lightweight and compact, these machines can be easily transported to various job sites, making them particularly beneficial for outdoor applications.
Environmental Considerations
- Cleaner Process: Handheld laser welding produces fewer fumes and emissions compared to traditional welding techniques, contributing to a cleaner working environment. This makes them suitable for sensitive areas like clean rooms or medical facilities.
- Reduced Need for Consumables: Unlike conventional welding methods that often require filler materials or gases, handheld laser welding typically eliminates these needs. This reduction not only decreases waste but also leads to additional cost savings.
Handheld laser welding machines offer remarkable precision, efficiency, and versatility while minimizing operational costs and environmental impact. Their growing popularity across various industries highlights their importance as an advanced solution for modern welding challenges.
Applications Across Industries of Handheld Laser Welding Technology
Handheld laser welding technology has become a crucial advancement across various industries, delivering exceptional speed, precision, and quality in welding processes. This innovative method is particularly beneficial in sectors where high-quality welds are essential for maintaining product integrity and performance. Below are the key industries that are leveraging handheld laser welding technology.
Automotive Industry
Efficient Component Joining:
Handheld laser welding is widely utilized for joining critical automotive components such as chassis, body panels, and exhaust systems. The precision of this technology ensures robust connections that can endure the demanding conditions of automotive applications.
Boosting Production Speed:
The rapid nature of handheld laser welding significantly reduces production time, which is vital in the competitive automotive sector where quick time-to-market is essential. This efficiency enables manufacturers to meet high demand while upholding quality standards.
Electronics Manufacturing
Safe Assembly of Delicate Components:
In electronics manufacturing, handheld laser welding is ideal for assembling sensitive components like microchips and circuit boards. The technology minimizes heat input, thereby reducing the risk of damage to delicate parts during the welding process.
Ensuring Quality Control Standards:
The high-quality welds produced by handheld laser machines comply with stringent industry standards, guaranteeing the reliability and functionality of electronic devices.
Medical Equipment Production
Creating Strong Seals:
Handheld laser welding plays a vital role in forming durable seals on stainless steel parts used in medical devices. This capability is crucial for maintaining both sterility and durability in medical applications.
Regulatory Compliance:
The precision offered by this technology aligns with strict regulatory standards in medical device manufacturing, thereby enhancing overall product safety and efficacy.
Kitchenware and Furniture Manufacturing
Durable Aesthetic Products:
This technology is commonly employed in crafting stainless steel kitchenware and furniture items. Handheld laser welding not only ensures strong welds but also provides aesthetically pleasing finishes that meet consumer demands for both functionality and design.
Versatile Design Applications:
The adaptability of handheld laser welding allows it to accommodate various designs, making it suitable for both functional kitchen items and decorative furniture pieces.
Aerospace Industry
Precision Welding of Lightweight Materials:
In aerospace manufacturing, handheld laser welding is used to join lightweight materials such as aluminum and titanium alloys. This technology delivers the precision needed to create complex components while minimizing weight, which is critical for aircraft performance.
Additional Applications
Handheld laser welding technology also finds applications in:
- Hardware Industry: Welding components like impellers and handles with high precision.
- Home Appliance Manufacturing: Used for welding parts such as refrigerator casings and microwave oven components, ensuring durability and aesthetic appeal.
- Metal Furniture Production: Enhancing the structural integrity of metal furniture while allowing for intricate designs without compromising on quality.
Handheld laser welding technology is revolutionizing production processes across these industries by improving efficiency, enhancing product quality, and enabling innovative design possibilities. Its ability to deliver precise, clean welds with minimal heat distortion makes it an invaluable tool in modern manufacturing practices.
Handheld Laser Welding vs. Conventional Welding
As manufacturing technologies progress, selecting between handheld laser welding and conventional welding methods becomes crucial. Each technique offers distinct advantages and disadvantages that impact efficiency, precision, and application suitability.
Overview of Welding Methods
Conventional Welding encompasses various techniques, including MIG (Metal Inert Gas), TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas), and Stick welding. This method utilizes an electric arc or gas flame to melt and join materials. However, it typically involves high heat input, which can lead to significant thermal distortion and a larger heat-affected zone (HAZ), potentially compromising the integrity of the welded materials.
In contrast, handheld laser welding employs a focused laser beam to create welds with minimal heat input. This process allows for precise control, resulting in clean and robust welds. The small HAZ generated during this method reduces the risk of warping or deformation in thin materials.
Key Differences
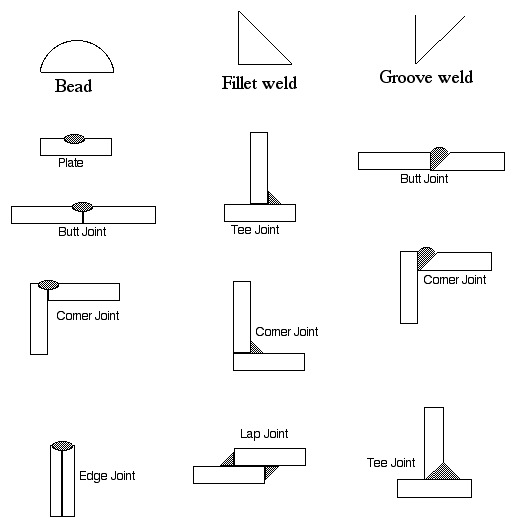
| Feature | Handheld Laser Welding Machine | Conventional Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Input | Low, focused heat minimizes damage | High heat can weaken surrounding areas |
| Precision | Extremely high precision for intricate designs | Depends on the welder’s skill |
| Thermal Distortion | Minimal due to rapid cooling | More prone to warping |
| Material Compatibility | Works with thin and exotic metals | Generally suited for thicker metals |
| Speed | Faster processes | Slower; requires setup |
| Versatility | Handles complex shapes easily | Effective for general tasks |
| Post-Weld Cleanup | Often requires no cleanup | Usually requires grinding |
Advantages of Handheld Laser Welding
- Efficiency and Speed: Handheld laser welding is significantly faster than traditional methods—up to four times quicker than TIG welding—boosting productivity in manufacturing environments.
- Precision and Control: The focused laser beam enables precise welds with minimal thermal distortion, making it ideal for delicate applications.
- Reduced Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ): The small HAZ minimizes the risk of material deformation, particularly beneficial for thin or sensitive materials.
- Versatility in Applications: This method is effective across a wide range of materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, and some plastics, making it suitable for industries like aerospace and medical device manufacturing.
- Lower Post-Weld Cleanup Needs: The clean nature of laser welds often eliminates the need for extensive post-processing.
Disadvantages of Handheld Laser Welding
- Higher Initial Costs: The upfront investment for handheld laser welding equipment is generally higher compared to conventional methods, which may deter some users.
- Maintenance Requirements: While operational costs may be lower over time, maintaining laser equipment can be more demanding than traditional welding machines.
- Skill Requirements for Setup: Initial configuration may require skilled personnel familiar with laser technology, even though operation becomes easier once set up.
Handheld laser welding offers numerous advantages over conventional methods, particularly regarding precision, speed, and reduced thermal distortion. However, the higher initial costs and maintenance requirements may pose challenges for some users. The choice between these methods should be guided by specific project needs, material types, and budget considerations. For applications requiring high accuracy and minimal distortion—such as in aerospace or medical device manufacturing—handheld laser welding is often the superior choice. Conversely, traditional methods may still hold value in larger-scale operations where cost-effectiveness is essential.
Conclusion
Handheld laser welding technology marks a transformative shift in the welding industry, providing substantial advantages over traditional methods. This innovative approach not only enhances speed and efficiency—operating up to four times faster than conventional techniques—but also ensures exceptional precision and control, making it ideal for intricate applications across various sectors.
Disclaimer
This content is compiled by OPMT Laser based on publicly available information for reference only; mentions of third-party brands and products are for objective comparison and do not imply any commercial association or endorsement.




