Schedule a Visit
Regardless of whether you require general advice or specific support, we are happy to help you.
Regardless of whether you require general advice or specific support, we are happy to help you.
All News
Share
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining is revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape, offering precision and efficiency that traditional methods simply cannot match. If you’ve ever faced challenges with inconsistent production quality or lengthy lead times, you’re not alone; many manufacturers struggle with these issues. OPMT Laser is here to help you navigate these challenges by providing insights into how CNC machining can streamline your operations and enhance product quality.
In this article, we’ll uncover the essentials of CNC machining, including its processes, benefits, and applications. Did you know that CNC machining can reduce production time by up to 75% compared to manual methods? This efficiency not only saves time but also significantly cuts costs. Join us as we explore how embracing CNC technology can transform your manufacturing capabilities and set you on the path to success.
CNC, short for Computer Numerical Control, denotes the automated control of machining tools via computer programming . These machines function using pre-programmed software instructions to execute tasks like cutting, shaping, and forming materials such as metal, plastic, or wood. This automated approach markedly improves production accuracy and consistency, minimizing manual involvement and human error.

CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines remain essential to modern manufacturing, providing precise automation of machining processes. The global CNC tools market is projected to exceed $100 billion. Understanding the operation of these machines involves several critical steps that contribute to their efficiency and accuracy.
The process starts with creating a Computer-Aided Design (CAD) model. Engineers use CAD software to design detailed 2D or 3D representations of parts. This initial step is crucial, laying the groundwork for all subsequent operations. A well-crafted CAD model ensures the final product meets specified design requirements, enhancing overall production quality.
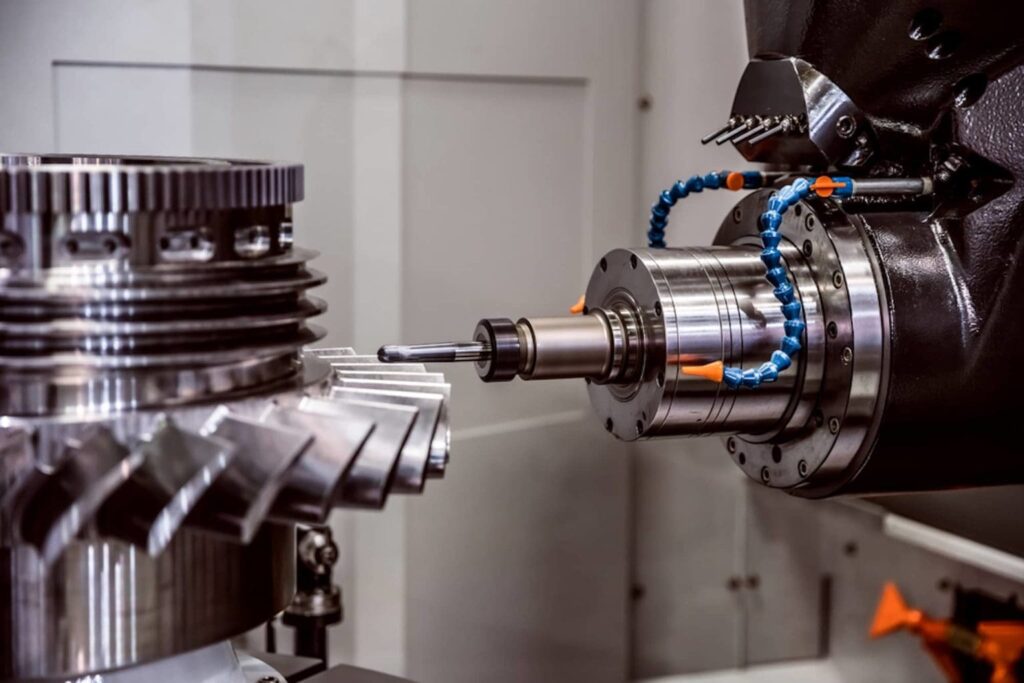

After the CAD model is complete, the next phase involves programming the CNC machine. This is achieved by converting the CAD design into G-code using Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software. G-code serves as a universal language that instructs the CNC machine on how to move and operate, detailing specific commands for actions like cutting and drilling. This programming step is vital for ensuring the machine executes tasks accurately and efficiently.
With G-code prepared, operators set up the CNC machine. This involves securing the workpiece onto the machine’s bed or fixture and inputting the G-code into its control system. Proper setup is essential for achieving accurate machining results, as misalignment can lead to defects.
Once set up, the CNC machine follows programmed instructions to perform operations such as cutting, drilling, or milling. It operates along multiple axes—typically X, Y, and Z—using stepper or servo motors to execute precise movements dictated by G-code. Multi-axis machining, especially with 5-axis machines, is increasingly common for creating complex geometries with fewer setups, which reduces production time and errors. In 2025, more CNC machines are equipped with robotic arms for automated loading and unloading, as well as automated tool changes, further minimizing human intervention.
Continuous monitoring during machining is crucial for maintaining quality standards . Operators monitor parameters such as speed and feed rates while assessing tool wear and surface finish quality. Real-time adjustments can be made to uphold precision and prevent defects . Modern CNC machines can achieve high accuracy, with some CNC mills and lathes producing parts with an accuracy of +/- 0.0025mm.
By mastering these steps—designing a CAD model, programming with G-code, setting up machines correctly, executing machining processes effectively, and monitoring performance—manufacturers can fully leverage CNC technology for enhanced productivity and quality in their operations.
For innovative solutions in CNC systems and laser processing, explore OPMT Laser’s offerings that optimize production processes for various industries. Check out our advanced products like Micro 3D Laser and 5-Axis Machining Centers for cutting-edge manufacturing capabilities.

CNC machines are essential tools in modern manufacturing, designed to enhance precision and efficiency across various applications. Here’s a closer look at the different types of CNC machines, highlighting their unique functionalities and uses.
3D printers fall under the CNC category despite their distinct additive manufacturing process. These machines create three-dimensional objects by layering materials based on digital designs. They are widely utilized for rapid prototyping, custom parts production, and even in medical applications like prosthetics. With advancements in technology, the capabilities of 3D printers continue to expand, making them invaluable in diverse industries. Interested in exploring innovative 3D printing solutions? Check out OPMT Laser’s Micro3D L530V for cutting-edge applications.
CNC lathes are engineered to produce cylindrical components by rotating the workpiece against a stationary cutting tool. This method allows for high precision in creating symmetrical parts such as camshafts and crankshafts, commonly found in automotive manufacturing. The automation of lathes significantly enhances production speed and accuracy, making them a staple in many machine shops. Have you considered how CNC lathes could optimize your production line? Learn more about our LP550V model for advanced machining capabilities.
CNC milling machines use rotating cutting tools to remove material from a stationary workpiece. They excel at performing various operations, including drilling, face milling, and contouring. This versatility makes CNC mills crucial in industries ranging from aerospace to electronics. The ability to create complex geometries with precision ensures that manufacturers can meet stringent design specifications. Curious about our milling options? Discover the 563V Vertical 5-Axis Machining Center for enhanced productivity.
CNC plasma cutters employ a high-energy plasma arc to cut through conductive materials with remarkable precision. These machines are particularly effective for thick metal sheets and are widely used in metal fabrication and construction industries. The speed and accuracy of plasma cutting make it an excellent choice for projects requiring intricate designs or large-scale production runs.
CNC routers are specifically designed for cutting softer materials such as wood, plastics, and composites. They are ideal for creating detailed designs and shapes, making them popular in woodworking, sign-making, and custom fabrication projects. The flexibility of CNC routers allows users to produce everything from furniture components to intricate signage with ease.
| Type | Functionality | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 3D Printers | Additive manufacturing for creating three-dimensional objects | Prototyping, medical devices |
| CNC Lathes | Rotates workpiece against a stationary tool for producing cylindrical parts | Automotive components, fittings |
| CNC Mills | Removes material using rotating tools for complex shapes | Aerospace components, electronic housings |
| CNC Plasma Cutters | Cuts conductive materials using plasma arcs | Metal fabrication, construction |
| CNC Routers | Cuts soft materials with high precision | Woodworking, signage production |
By understanding the distinct capabilities of each type of CNC machine, manufacturers can select the appropriate technology to meet their specific needs effectively. OPMT Laser is committed to providing innovative CNC systems and laser processing solutions tailored to enhance production efficiency across various industries. Explore our range of products today!
CNC machining is renowned for its unmatched precision and repeatability. The integration of computer-controlled processes ensures that each component is crafted to exact specifications, significantly minimizing the risk of human error. This exceptional accuracy is vital in various industries, particularly those requiring strict tolerances for optimal safety and functionality. For instance, manufacturers can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.001 inches, which is essential for producing high-quality components that meet rigorous standards.
The efficiency of CNC machining is a game-changer in modern manufacturing. These machines can operate continuously, often running 24/7 without breaks, which leads to significantly higher output rates compared to traditional methods. Automation reduces setup times and allows for rapid production cycles, enabling manufacturers to fulfill large orders swiftly while minimizing downtime. In fact, businesses utilizing CNC technology can increase their production rates by up to 50%, making it an attractive option for both large-scale and small-batch manufacturing.
One of the standout features of CNC machining is its ability to minimize material waste. The precise cutting capabilities ensure that raw materials are utilized efficiently, resulting in less scrap and lower costs. This not only contributes to significant cost savings but also aligns with sustainability initiatives by reducing the overall environmental impact of manufacturing processes. For example, companies can achieve up to 90% material utilization rates, demonstrating the technology’s role in promoting eco-friendly practices.
CNC technology significantly enhances workplace safety by reducing human involvement in potentially hazardous tasks. With machines performing most operations autonomously, the risk of accidents decreases dramatically. Operators can monitor multiple machines from a safe distance, ensuring a secure working environment while maintaining high productivity levels. This shift not only protects employees but also fosters a culture of safety within manufacturing facilities.
CNC machines offer remarkable versatility; they can be quickly reprogrammed to produce different parts or adapt to new designs without extensive downtime. This flexibility makes CNC machining suitable for both mass production and custom projects, allowing manufacturers to respond rapidly to changing market demands or specific customer requirements. For instance, a single CNC machine can switch between various products in a matter of minutes, significantly enhancing operational agility.
By leveraging these advantages, OPMT Laser provides innovative CNC systems and laser processing solutions that meet the diverse needs of modern manufacturing while ensuring efficiency and sustainability in every project. For more information on our products, explore our range of advanced CNC solutions like the Micro3D L530V or the LP550V.
A CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machinist is a crucial professional in the manufacturing sector, responsible for operating and maintaining CNC machinery to produce high-precision parts and components. Their expertise ensures that manufacturing processes are efficient, reliable, and yield high-quality outputs across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and healthcare.
To succeed as a CNC machinist, several key skills and qualifications are essential:
CNC machinists play an integral role in modern manufacturing environments. Their expertise not only ensures that machinery operates effectively but also contributes significantly to the production of high-quality components essential for various applications. With the increasing reliance on automation in manufacturing processes, the demand for skilled CNC machinists continues to grow.
CNC machining is revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape, offering unparalleled precision and efficiency. If you’re curious about how this technology can enhance production processes, you’re not alone—many industries are embracing CNC to streamline operations and improve product quality. With CNC machining projected to grow by over 6% annually, now is an exciting time to explore this field.
At OPMT Laser, we provide cutting-edge solutions that empower you to harness the full potential of CNC technology. Whether you’re interested in our advanced 5-axis machining centers or laser cutting machines, there’s a wealth of opportunities waiting for you. Ready to take the next step in your manufacturing journey? Explore our offerings and discover how OPMT Laser can help you stay ahead in this innovative industry!
Disclaimer
This content is compiled by OPMT Laser based on publicly available information for reference only; mentions of third-party brands and products are for objective comparison and do not imply any commercial association or endorsement.
Explore the world of CNC machining as we compare 3-axis and 5-axis technologies. From basic operations to complex geometries, find out which machine suits your manufacturing needs in 2025.

Explore OPMT’s proven 5-phase ODM process for custom laser systems. ISO-certified manufacturing, ±0.003mm precision, IP protection. Submit project requirements today.

Looking for the best 5-axis CNC machining center suppliers? Check our top 10 list for expert insights and find the perfect fit for your needs!

Explore the top 10 laser metal cutting machines of 2025, featuring industry leaders like Trumpf, Bystronic, and OPMT Laser. Compare cutting-edge technology, precision, and efficiency to find the perfect solution for your manufacturing needs.
Please fill in your contact information to download the PDF.

